Types of Music Licensing for Film and Video Production
Feb 16, 2024
Are you a filmmaker or content creator and are confused about the legalities and minute details of obtaining licenses for music or background scores?
Yes, it can get baffling, as music licenses are tricky and it’s important to know all the nitty-gritty of it so you don’t do anything illegal, even mistakenly.
For example, The Beatles filed a $15M lawsuit against Nike for using their song "Revolution" in a television commercial without obtaining proper licensing. Similarly, there have been many cases like Warner/Chappell Music vs. Good Morning to You Productions Corp. (2015) and Ray Parker Jr. vs. Huey Lewis and the News (1984), where Murphy’s Law proved to be true.
What is Music Licensing?
The term music licensing refers to the process of getting legal rights to use or perform copyrighted music on multiple media platforms that include films, videos, TV shows, TV advertisements, and other forms of audiovisual productions.
When filmmakers or video producers plan to use music in their work products, either in the opening, closing, or interspersed scenes, they must procure the proper licenses from the copyright owners, usually the music publishing industry, record labels, or individual artists.
As a film/video professional, music licenses are extremely important for you because of the following reasons:
Legal Compliance: Ensure adherence to copyright law by licensing music properly, avoiding infringement, and respecting creators' rights.
Protection: Secure licenses to demonstrate legal rights and prevent potential copyright disputes.
Quality: Enhance projects with professionally composed music that complements the atmosphere and theme.
Flexibility: Choose from diverse musical styles to enhance creativity and storytelling.
Monetization: Enable revenue generation through proper licensing for distribution channels.
Types of Music Licenses
Master License
Master license means you have a right to use the particular recording of the same song with specific terms and conditions. This generally means that it comes from the copyright holder of the master recording, which is likely to be an artist’s record label like it is of a recording artist.
https://youtu.be/M5adQwYc7_c?si=XFSB4pxmznHFRoXR
Mechanical License
Through this license, it becomes legal to record a musical work in audio forms that can be in digital downloads, CDs, or streaming services. If a song is reprinted in writing without the consent of the music publisher or using a mechanical rules agency, mechanical licenses are often transferred.
https://youtu.be/Kqffbk9Dm5M?si=K_nDWa5aXYRtf_Sp
Synchronization License
Sync license allows you to synchronize a music composition with a given video production. It means that you have an opportunity to choose any kind of music for your movie or short film.
Usually, a sync deal goes through the bargaining cycle probably between the filmmaker and the music rights owner negotiations, which involve terms such as territory, duration, and media use.
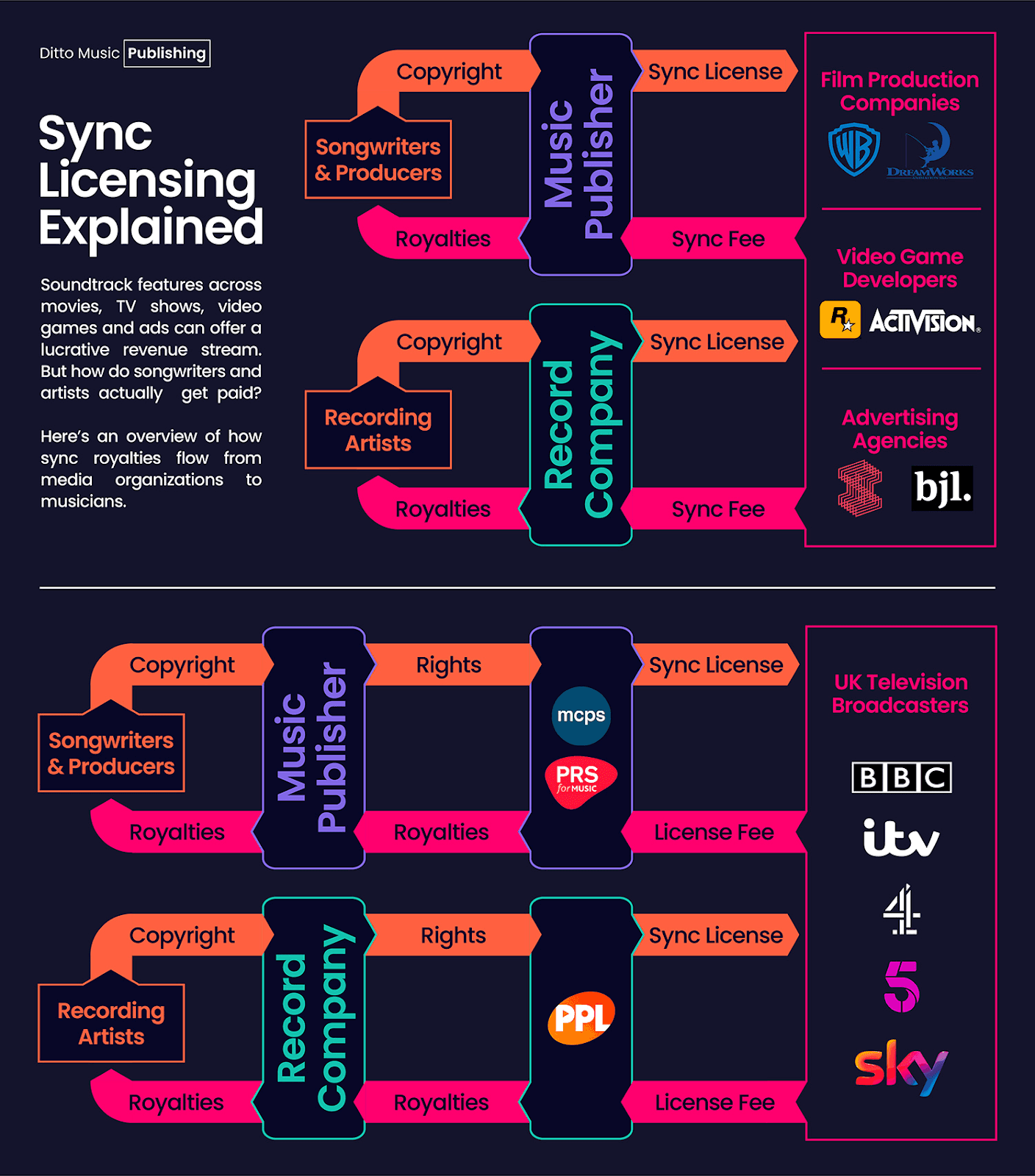
Public Performance License
Public Performance License (PPL) is publicly displaying a piece of music that is playable in a theater, say at a televised public event, or on the TV.
It is the PROs that usually possess the authority to license public performance rights, such as ASCAP, BMI, and SESAC, where they handle royalty payments for songwriters and music publishers.
Theatrical License
A theatrical license grants permission to publicly perform a copyrighted work in a theatrical setting, such as a stage play, musical, or live performance. So if you intend to film a live musical or play, you will be required to obtain this license.
Creative Commons License
Some artists and composers release their music under Creative Commons licenses, allowing various levels of free use with certain conditions. However, it's crucial to carefully review the specific terms of the Creative Commons license to ensure compliance with your intended use.
Print Rights License
A print rights license grants permission to reproduce and distribute copyrighted material in print format.
This type of license is commonly used in publishing, where authors or publishers obtain the right to print and distribute books, magazines, newspapers, or other printed materials that contain copyrighted content.
So, if you intend to use the songs’ lyrics as promotional material or want to distribute physical CDs of your film’s soundtrack with lyrics printed on it, you will need to obtain this license.
Production Music Library License
Production libraries of music ensure essay writing, especially composed and published tracks that are free from distribution hassle and can be used for feature films, TV, and video production.
That way, licensing agreement processes become easier and not tight, as it usually are when one obtains a commercial tracks license.
Needle Drop License
This kind of license negotiated is often used in television and radio productions, where music is diffused continuously, and the licensee pays a fee for using the music with every repetition (similar to a "per use" principle).
How To License Music?
You can follow a step-by-step process to obtain licenses for music and get permitted by law to use copyrighted music or compositions.
Firstly, it’s important to find and investigate the recipients, who may be songwriters, producers, music publishers, record organizations, or performing rights organizations (PROs), to identify them.
As the next step, you need to identify rights holders and then negotiate terms to come to terms with them. Usually, an agreement between parties involves talks on the length, diaspora, media utilization, royalties, and other necessary issues at stake.
When the parties arrive at an agreement, is the next step to secure a written license contract that is a good proof and liability of the agreement. The step of making payment for the licensing fees or royalties, if there are any, is after it.
Compliance is irrevocably important. Steps such as the tracking of licensing use, the proper credits and referencing of the producers, and the renewing or extending the licenses are obligations you’ll need to follow.
Keeping in touch with the rights holders and seeking legal help when needed maintains smooth movement through the intellectual property exploitation terrain.
That leads to using copyrighted music ethically and according to laws in personal projects by filmmakers, video makers, and producers while respecting the rights of those whose talents were used.
Also note that these licenses and compliances vary from state to state and country to country, so be mindful of that! A lawyer specializing in music rights licensing usually knows all these steps and also has the required contacts and resources for obtaining a music license.
Otherwise, if all of this sounds like too much hassle, you have music licensing companies like Musicbed, Soundstripe, Epidemic Sound, Artlist, etc., who can take care of all these steps for you.
Custom Music as an Alternative
In addition to traditional licensing options, filmmakers and content creators have the option of exploring custom music as an alternative. Custom music offers a unique and tailored approach to scoring your film or video project, allowing you to work closely with composers to create original pieces that perfectly complement your narrative and visual elements.
One notable music agency specializing in custom compositions is Media Music Composer. With a team of skilled composers and a diverse range of musical styles, Media Music Composer aims to provide filmmakers with bespoke soundtracks that enhance the overall quality and impact of their projects. Collaborating with such agencies allows for flexibility in choosing or crafting music that aligns seamlessly with the atmosphere and theme of your work, offering a personalized touch that can set your production apart.
Custom music not only ensures legal compliance but also provides an opportunity for filmmakers to express their creative vision through a unique auditory experience. Consider exploring the option of custom music through agencies like Media Music Composer for a distinct and memorable soundtrack for your next project.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricate landscape of music licensing is crucial for filmmakers and content creators to ensure legal compliance and respect for the rights of music creators. In addition to exploring traditional licensing avenues, the option of custom music emerges as a unique alternative, allowing filmmakers to collaborate with agencies like Media Music Composer for bespoke soundtracks that elevate the overall quality of their projects. This personalized approach not only enhances the creative vision but also ensures legal adherence. Whether opting for traditional licensing or custom compositions, it is essential to consult with legal professionals or licensing companies for a comprehensive understanding of the rights and obligations involved. As the complexities of music licensing may vary across states and countries, diligent research and legal guidance remain imperative in this creative process. Ultimately, by navigating these considerations ethically, filmmakers can use music to enhance their projects while respecting the talents of the creators involved.


